Parkinson disease(uptodate
19.3)
치료
치료의 시기 결정
dominant hand에 영향이 있는가
일을 방해하느냐, 일생생활에 영향을 미치는가, 사회활동에 영향
현저한 bradykinesia가 있는가, 걸음걸이에 영향이 있는가
약에 대한 개인적인 철학에 따라서.
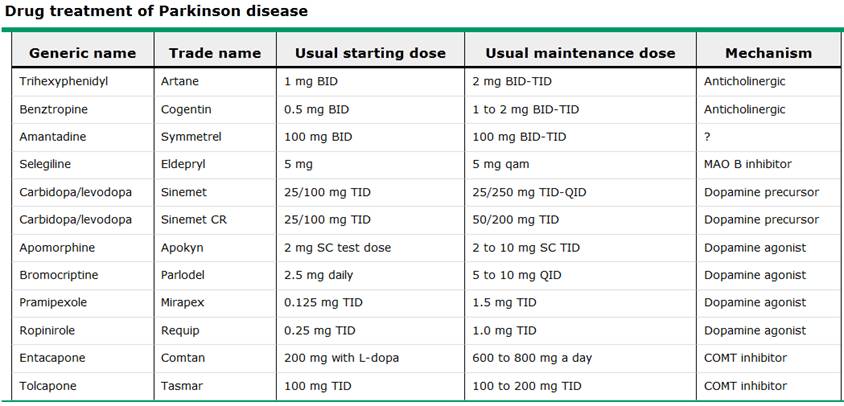
Available therapy
1. levodopa(idiopathic PD, lewy body PD에서 가장 효과적임) 타제제로 조절이 되지 않을때 쓰자. akinetic symptom과 rigidity, tremor에 효과적이나, postural instability에는 효과가 적다.
peripheral decarboxylase inhibitor
1.carbidopa (BBB를 통과하기전에 dopamine으로 전환되는 것을 억제하여, nausea/vomiting ,orthostatic hypotension억제) 와 combination : (levodopa-carbidopa)Sinemet
2. benserazide : (levodopa-benserazide)madopar
부작용
nausea, somnolence(졸림) , dizziness, headache (이것들이 심각하지는 않다)
가장 심각한 부작용 : confusion, hallucinations, delusion,m agitation, psychosis
small dose로 시작 carbidopa-levodopa 25/100의 1/2T로 bid~ tid로 시작함
(부작용이 없다면 psychosis)1/2T를 1T tid 될때까지 몇주에 걸쳐서 titrating
이후 lowest levodopa dose로 titrating
처음먹을때는 음식과 함께 복용(초기부작용인 구역을 막기 위해서)
CR(controlled) 제제나, SR(sustained)제제는 IR제제보다 30%효과가 적다. 천천히 brain level 올라가므로
그래서 처음 사용시 reponse assess에 적합하지 않다.
첫 시작은 IR제제로 하고 이후 CR, SR제제로 change
몇년간의 사용을 보면 IR, CR,SR제제 모두 같은 용량에서 효과는 같다.
첫사용시 nausea 가 있다면 carbidopa가 부족해서 생긴것으로, carbidopa의 용량을 보충하던지, antiemetics를 쓰되 dopamine antagonist인 metoclopramide, prochlorperazine을 쓰면 안된다. domperidone을 써라.
그외 부작용 : homocysteine level을 높여 hip fracture증가
methylmalonic acid 증가로 인한 sensorimotor peripheral neuropathy
Motor
fluctuations(the wearing-off phenomenon)
involuntary movements known as dyskinesia, abnormal cramps and postures of the extremities and trunk known as dystonia, and a variety of complex fluctuations in motor function
원인 추정 : due to progressive degeneration of nigrostriatal dopamine terminals 로 인하여 serum 도파민 레벨에 대한 buffering이 떨어져서
또다른 원인 추정 levodopa의 oxidative
stress and accelerated neurodegeneration
levodopa쓰고 몇년후에 발생(5~10년후에 50%에서 발생)
low dose 쓰면 20%에서 발생
young -onset에서 더 많이 발생
levodopa 및 dopamine agonist에서 다 생길수 있다. initial Tx를 pramipexole로 한 것이 levodopa로 한것보다 덜 생겼다
따라서 필요양보다 high dose Dopaminergics는 피해야한다.
될수 있는데로 levodopa의
치료를 늦추라고 제안
Acute akinesia
몇일지속되고, 약물에 반응을 안한다
Neurotoxic versus
neuroprotective effects
substantia nigra의 도파민 neuron의 퇴행을 가속화시키지 않을까 하였으나, 아닌것으로 결론냄
consensus의 결론
- There is no evidence that
levodopa causes neuronal death in animal models of parkinsonism
- The relevance of in vitro
studies of levodopa toxicity to clinical use of levodopa is highly
uncertain
- There is no evidence that
chronic administration of levodopa exacerbates the degenerative process in
PD
- Late motor complications
arise due to the combination of progressive degeneration of dopamine
neurons and the reversible effects of levodopa administration
2. MAO B inhibitor
Selegiline
증상 조절에 moderate 로 효과적
neuroprotective effect
단독으로 쓸때는 significant한 이득은 없다
초기 PD에서는 합리적인 선택이 될 수 있다.
용법 : 현재 추천 selegiline 5 mg 아침에 하루 한번
10mg/day 이상의 용량은 추가적인 이득이 없고, non selective MAO 억제를 일으킬수 있어, tyramine 포함한 음식을 먹었을때 상호작용으로 고혈압성 위기가 발생할 수 있다.
다른 nonselective MAO inhibitors와는 달리 selegiline 은 tyramine-containing foods를 먹어도 고혈압성위기를 유발하지 않는다.
Adverse effects
levodopa 가 유발하는 부작용인 dyskinesia and psychiatric toxicity를 증가시킬수 있다.
Nausea and headache
insomnia, confusion(고령)
TCA와 SSRI와 같이 사용하지 말것
3. DOPAMINE AGONISTS
bromocriptine, pramipexole, ropinirole, rotigotine, and injectable apomorphine등이 있다.
Apomorphine and lisuride(IV)
additional DAs : acute Akinetic 에피소드에서 rescue therapy로 쓸수 있다.
대부분 IR levodopa보다 작용기간이 길다
effective in patients with advanced PD complicated by motor fluctuations and dyskinesia
ineffective in patients who have shown no therapeutic response to levodopa.
effective as monotherapy in
patients with early disease
early DA monotherapy postpones the future onset of motor complications
less potent than levodopa
일부전문가들은 60세 이전에 initial tx로 쓰자
Antiemetic therapy (eg, with trimethobenzamide) is initiated three days prior to starting apomorphine
Dosing — The DAs
generally require administration at least three times a day at maintenance
doses:
- Bromocriptine is
usually started at 1.25 mg twice a day; the dose is increased at two to
four week intervals by 2.5 mg a day. Most patients can be managed on 20 to
40 mg daily in three to four divided doses, although total daily doses as
high as 90 mg can be used.
- Pramipexole is
usually started at 0.125 mg three times a day. The dose should be
increased gradually by 0.125 mg per dose every five to seven days. Most
patients can be managed on total daily doses of 1.5 to 4.5 mg.
- Ropinirole is
usually started at 0.25 mg three times a day. The dose should be increased
gradually by 0.25 mg per dose each week for four weeks to a total daily dose
of 3 mg. Most patients can be managed on this dose. After week four, the
ropinirole dose may be increased weekly by 1.5 mg a day up to a maximum
total daily dose of 24 mg. Benefit most commonly occurs in the dosage
range of 12 to 16 mg per day.
- Pramipexole and
ropinirole are
now both available in sustained release formulations; these are useful for
convenience and for avoiding peaks and troughs in plasma levels.
- Transdermal rotigotine is
available in Europe. It is a once-daily patch that is usually started at 2
mg/24 hours and titrated weekly by increasing the patch size in 2 mg/24
hour increments to a dose of 6 mg/24 hours.
Adverse
effects of dopamine agonists
similar to those of levodopa, including nausea, vomiting, sleepiness, orthostatic hypotension, confusion, and hallucinations
Dopamine agonist withdrawal syndrome
cocaine withdrawal과 비슷하다.
only responded to resuming the DA.
4. COMT INHIBITORS
tolcapone (Tasmar) and entacapone
단독사용시
비효과적이다.
레보도파의 효과를 강하게 하고 연장시킨다.
레보도파의 용량을
30% 줄인다
mainly used to treat
patients with motor fluctuations who are experiencing end-of-dose wearing
"off" periods
Dosing — The starting dose of tolcapone is 100 mg three times daily; the clinical effect is evident immediately. The dose of entacapone is one 200 mg tablet with each dose of levodopa, up to a maximum of eight doses per day
Adverse effects
dyskinesia, hallucinations, confusion, nausea, and orthostatic hypotension
managed by lowering the dose of levodopa either before or after the addition of tolcapone
Diarrhea
orange discoloration of the urine
5. ANTICHOLINERGICS
most useful as monotherapy in patients
under age 70 with disturbing tremor who do not have significant akinesia or gait disturbance
advanced disease who have persistent tremor
despite treatment with levodopa or DAs
Dosing — Trihexyphenidyl is
the most widely prescribed anticholinergic agent, although there is little
evidence to suggest that one drug in this class is superior to another. The
starting dose of trihexyphenidyl is 0.5 to 1 mg twice daily, with a gradual
increase to 2 mg three times daily. Benztropine traditionally
is more commonly used by psychiatrists for the management of antipsychotic
drug-induced parkinsonism; the usual dose is 0.5 to 2 mg twice daily.
Adverse effects
memory impairment, confusion, and
hallucinations
6. AMANTADINE
relatively weak antiparkinsonian drug with low toxicity that is most
useful in treating patients with early or mild PD
Its mechanism of action is uncertain
it is best used as
short-term monotherapy in those with mild disease
little benefit when added to levodopa
more effective than anticholinergic drugs for akinesia and rigidity
reduce the intensity of levodopa-induced dyskinesia and motor fluctuations
처음부터여기까지 uptodate 19.3