수면제
cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) as the initial therapy(uptodate19.3)
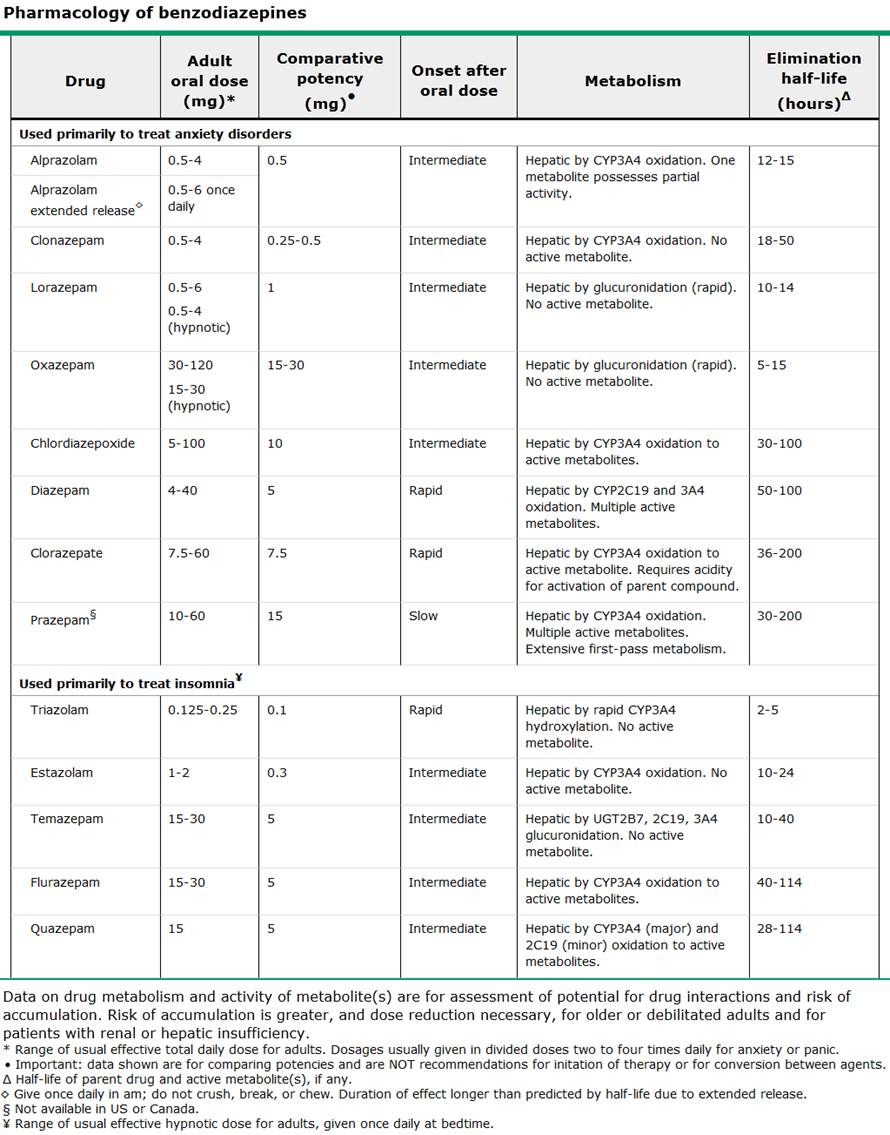
여기부터 국시책-------------
quazepam
flunazepam
trazolam
estazolam
temazepam
로라제팜, diazepam을 수면제로 처방하지 못할 특별한 이유는 없다
zolpidem
수면제로 공인되지 않았지만, 불면증에 처방되는 약물
진정성 항우울제
melatonin
항히스타민제
------------------------------
여기부터 uptodate19.3----------------------------------------------------
Barbiturates are now largely limited to induction of anesthesia
Although the clinical effects of the benzodiazepines resemble and overlap with other sedative-hypnotics, benzodiazepines are more specifically anxiolytic.
benzodiazepine
Benzo계열
작용
onset까지의
시간을 줄여줌
stage2 sleep을 늘림
stage4수면을 억제(night terror가 stage4에
일어남 : 치료 diazepam)
총 수면시간을
늘림
상대적인
REM 시간을 약간 줄임
sleep latency를 줄임
awakening의 수를 줄임
수면
질을 좋게함
Benzo계열
부작용
short acting을 쭉 쓰다가 stop하면 rebound insomnia발생가능
(long acting을 쓰면 withdrawl이 덜하다, clonazepam 은 long elemination half life를 가지므로 withdrawal의 치료에 쓰인다 : 수면과는 별개의 이야기로 benzo전체적인 특징에서 나오는 이야기, uptodate19.3)
trazolam은 anterograde amnesia(특히 알콜과 같이 섭취시)
agressive behavior
sleep waking(드물다)
benzo계열의 일반적인 부작용파트
Reinforcement (abuse
혹은 liked) : addiction history가
없는 사람에서는 강화 없음
abuse history가 있는 사람에서는 약한 reinforcers
알콜중독이나 다른약물중독자들에서 자주 abuse됨
withdrawal sx : seizure, status
epilepticus
Other symptoms of withdrawal
include:
- Increased body
temperature
- Elevated blood pressure
- Increased respiratory
rate and heart rate
- Aroused level of
consciousness or frank delirium
- Tremulousness
- Increased reflexes
- Disorientation
- Psychotic behavior
including hallucinations.
내성(효과가 약해서 양을 늘리는것) : sedation , euphoric effect : 급하게 내성이 발생. 몇일만에
anxiolytic , imsomnia에 쓰는것은 내성이 생기지 않는다.
수면제로 내성이 생긴다(신경정신의학2판)
심리적의존과 신체적의존이 있다(신경정신의학 2판)
long-acting
일반적으로 불면증에 쓰이지 않는다. 효과가 길기 때문에
can lead to the accumulation of active metabolites.
The long-acting benzodiazepines 은 고령에서 피해야한다.
Nonbenzodiazepines
more targeted action at one GABA type A receptor : less anxiolytic and anticonvulsant activity
zaleplon, zolpidem, eszopiclone, and zolpidem extended release
부작용은 benzodiazepine 계열과 비슷하나, frequency와 severity는 덜하다. 이유는 short half-life때문
내성 의존성이 벤조계열보다 작다(신경정신의학 2판)
매우 짧은 반감기 , 대략 한시간
수면 시작이 어려울때
수면 유지에는 효과없음
hangover , rebound insomnia는 없다.
S/E : 두통, 어지러움, 구역, 복통, 졸림
장기간사용은 승인되지 않았다.
반감기 대략 1.5~2.4 시간
수면시작이 어려울때 단기 치료로 쓰임
hang-over나 rebound insomnia는 없다.
S/E : 두통, 어지러움, 졸림, hallucination
장기사용으로 승인되지는 않았다.
Zolpidem extended
release
역시 반감기는 1.5 to 2.4 hours
longer duration.
sleep onset insomnia and sleep maintenance insomnia
hang over는 없다
Side effects는 regular zolpedem에 비해서 상대적으로 적다
headache, somnolence, dizziness
단기간 사용에만 제한 된 것은 아니다.
남용이나 의존의 증거는 거의 없다
이론적으로 장기간 사용시 습관성이 될 수 있다.
nonbenzodiazepines 중에서 가장 긴 half-life 5~7시간 , 노인에서는 9시간
시작과 유지에 모두 효과적
metalic taste
hang-over는 없다
S/E
졸림, 두통, 어지러움, 불쾌한 꿈
단기간 사용에만 제한 된것은 아니다.
남용이나 의존의 증거는 거의 없다
이론적으로 장기간 사용시 습관성이 될 수 있다.
Melatonin agonists — Ramelteon
half-life of 1.5 to 5 hours
Ramelteon 은 benzo나 nonbenzo에 비해서 side effect가 작다
hangover effect 없다
habit forming 없다
Other medications
Antidepressants
amitriptyline, trazodone, doxepin
우울증과 연관된 불면에서 사용하면 좋다
우울증과 연관되지 않은 불면에서는 low dose doxepin외에 사용은 추천되지 않는다
Onset of action sleep aid: 1-3 hours
Half-life elimination: 7-10 hours
Diphenhydramine
Routine use of diphenhydramine to treat insomnia is not recommended
Antipsychotics
The routine use of antipsychotics to treat insomnia in patients without psychosis is not recommended
Barbiturates
Routine use of barbiturates to treat insomnia is not recommended
Over-the-counter
Valerian(허브)
Melatonin
delayed sleep phase syndrome
low melatonin levels
두가지에서만 benefit이 있다.
처방약
For patients with sleep onset insomnia
zaleplon, zolpidem, triazolam, lorazepam, and ramelteon.
sleep maintenance insomnia
zolpidem extended release, eszopiclone, temazepam, estazolam, and low dose doxepin
Combination therapy involves prescribing both cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and a medication
Continuing CBT alone after the completion of initial therapy appears to be the best option for maintaining improvement long-term.
여기까지 uptodate 19.3