ºñ´¢±â°ú °Ë»ç¹æ¹ý
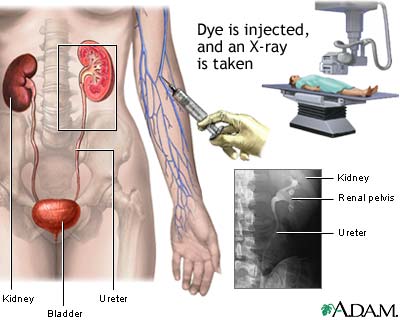
IVP
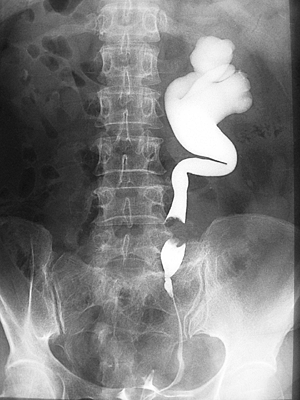
VCUG
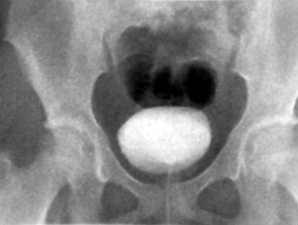
foley Ä«Å×ÅÍ °°Àº °ÍÀ¸·Î ¹æ±¤À» contrast ¹°Áú·Î ä¿îÈÄ ¼Òº¯À» º¸°ÔÇϸé¼
fluoroscopy(¿¬¼ÓÀûÀÎ ÃÔ¿µ)·Î º»´Ù
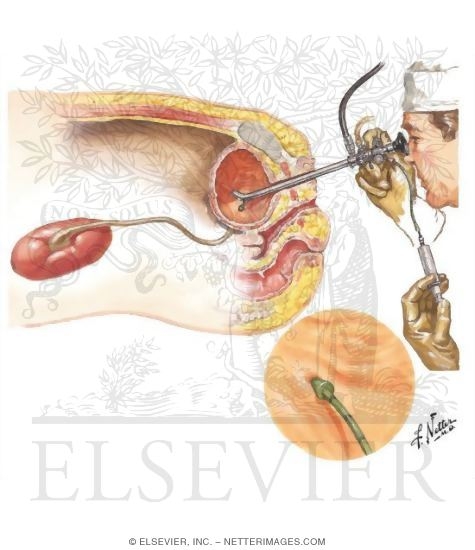
Retrograde pyelography
Retrograde pyelography combines the use of a long, flexible
viewing tube called a cystoscope with contrast x-rays to visualize the kidneys
and ureters. The cystoscope is inserted through the urethra into the bladder;
fiberoptic cables permit direct visual inspection of these structures. A
catheter is then threaded through the scope so that a contrast dye can be
infused directly into the ureters to delineate them on x-ray films. Retrograde
pyelography is most often performed when intravenous pyelography produces
inconclusive results, or when it cannot be performed because of impaired kidney
function or another reason.
¹æ±¤°æÀ¸·Î º¸¸é¼ ´ÙÀ̸¦
ureter¿¡ ¸ÂÃç¼ ½ð´Ù. ±×·¯¸é¼
fluoroscopy·Î ÃÔ¿µÇÑ´Ù
½Å±â´ÉÀÌ ³ªºü¼ IVPÇϱ⠾î·Á¿ï¶§, IVP°Ë»ç °á°ú°¡ ¾Ö¸ÅÇÒ¶§
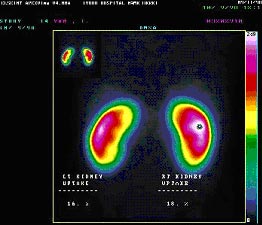
DMSA(APNÀÇ Áø´Ü¿¡ ¸Å¿ì sensitive)
radionuclide
emits a type of radioactivity called gamma ray
injection into a vein
DMSA is used because it builds up concentrate in the kidneys
areas of the target organ or tissue which emit lots of gamma rays may be shown as red spots ('hot spots')
¸ñÀû : to check the structure of the kidneys, their size and shape
children who have had urinary tract infections
areas of the kidney are working well and any areas of scarring
Scarring can be caused by a condition in which urine travels back from the bladder to the kidneys. This is called vesico-ureteric reflux
also look for reduced blood supply to the kidneys.
DMSA does not attach itself to areas of the kidneys that are damaged.
monitor any changes to inflammation of the kidneys.